|
|
Yard: History
Buildings with compound in Iran have a precedence of about 8000 years. The various buildings and houses have passed a time of approximately 6000 years until attaining to the complete central compound area.
Courtyard, in various historical era, has had one or more application of the foregoing titles.
The most primitive way of encircling a refuge inside a stockade could be seen in the stone fences of Azerbaijan. Those stockades, though not high, but have a sign of distinguishing the limit of ownership by constructors. Those stockades still could be seen in regions of Iran such as Guilan plains and rustic mat covered with a fence called “the house”.
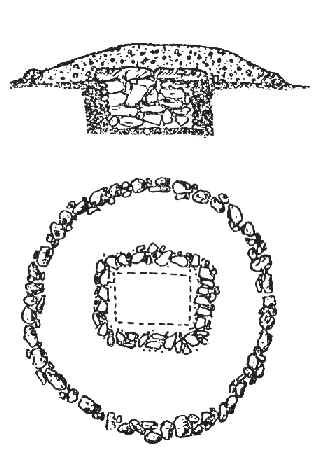
Stone Fence
Courtyard have been excavated as a connected element among spaces in ancient houses of Tappeh Zagheh (6th millennium B.C.)
Houses consist of 2 parts “compound” and “covered” with residential spaces and non-residential places. The first (residential) were divided to two sectors for repose and sleeping and daily activities, keeping livestock or restoring agriculture products, fold, pen, kitchen and some stores were built in the yard. All houses had some two three yards.
In this very place, a sample of a very simple yarded house, with one single room and small storage, is considered as a primitive quest to form a compound yard, in better feature and very near to central yard, is excavated in a building named “Sakhteman Soukhteh” (meaning: burnt building), in “Tappeh Hessar” of “Damghan” this building has had a defensive stockade, tower and rampart in distances. Various spaces like central hall, storages, kitchen and some other rooms, were opened towards the yard.
Another building named “Sakhteman Soukhteh” in the ancient hill of Hassanlou, (800-1000 B.C.) was built with the yard. A lateral specialty of this building, is its having two yards through one residential space.
Chaghazenbil was first built with a central yard. This building had a central yard in lower floors; each yard had reposing space, bathroom and kitchen around themselves. Probably houses in the ancient city of “Susan”, had also an open (or closed) central space, so that other spaces were opened towards it.
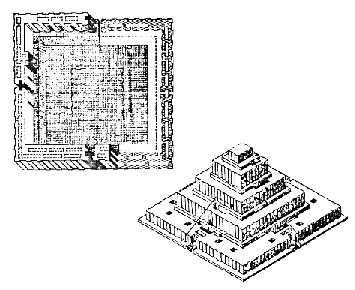
Chaghazenbil
Parthian, have utilized central yard in their architecture, their remaining works in Kuh Khajeh in Systan and Ashur confirms the aspect.
In Kuh Khajeh, building of a palace with central yard and two verandas is excavated; spaces of some part of the palace, were opened toward the yard, but had no visual connection looking outside.
Assyrian Palace of the first and second century, had also the same specification in the plan, having four verandas on four sides of yard. Iranian architecture researches have introduced this design as a pattern for construction of Four-Verandas Mosque with central yard in the outset of Islam.
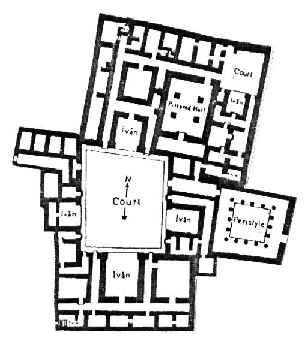
Assyrian Palace
This method of construction was applied later, in Fire Temple of "Firouzabad". This great building have three domes and lateral spaces and also a central yard.
Sassanids, in continuation of Parthian buildings, have built big buildings with yards, like "Sarvestan Palace", "Kasra Palace" in Tisfoun and "Khosro Palace" in Qasre Shirin.
This type of construction (building with central yard), was followed in Islamic era and some of big mosques in beginning of Islam were built in this way. Some important works of Islamic outset with this design are: Mosque of Fahraj (8th century A.D.), Tarikhaneh Mosque of Damqan and Mosque of Nain.
In the following periods, distinguished sample of Iranian mosque were introduced with four verandas and central yard.
There is not much samples of house plans of Iran in outset of Islam, but it is probable that in some parts of country, houses were built stressing mostly at introverts. Houses of two far away buildings in Gorgan and Siraf have also their yards.
One of the most ancient houses, remained from 14th century AD., in Iran, is House of Taq Bolandha, in Nahadan Quarter of Yazd. House has a vestibule and spiral corridor. Main fronts of the house are in two sections, sun-looking and sun backed; also some spaces were built in Eastern and Western fronts; one of the particularities of this house is application of four-section-ceiling as a cover of some spaces of house.
There are many houses with yard, remained from Safavid era, in Isfahan. Shiraz has also many houses from Zand era. Also, one could find pretty houses, specially in Kashan, Shiraz, Yazd and other cities, as a souvenir of Qajar era, in which central yard is formed by setting side by side the various spaces of house.
|
|



